
Hello everyone! Today, let’s dive into the world of Python – the Tony Stark of the programming world. We’ll begin by exploring its key concepts and covering all the fundamental knowledge you need for your programming journey. Of course, we can’t encompass everything in just one blog post, so remember to stay tuned as we publish more content. In this blog “Introduction to Python Programming – a Guide”, I’ll explain the fundamental basics of Python, or any programming language for that matter. So, let’s get started without any delay.
Alright everyone, let’s quickly introduce ourselves to the language before delving into Python’s key components. This way, we can all become more familiar with it.

Guido van Rossum released Python, a high-level programming language, in 1991, gaining widespread popularity due to its simplicity and versatility. Python’s syntax emphasizes clarity and conciseness, making it easy for programmers of all levels to learn and understand. It also focuses on readable code, enabling collaboration in large projects.
Fun fact: Python wasn’t named after the snake but after the British comedy group Monty Python. Guido van Rossum, a fan of the group, paid homage by naming the language after them. So, when you use Python, remember it’s named after comedians, not reptiles!
Alright everyone, before we dive deeper into Python’s key components. Let’s take a moment to explore some of the language’s key specifications that make it so robust. It’s important to have a solid understanding of what we’re getting into before diving in headfirst and learning a new language. So, let’s take a closer look at what makes Python such a powerful programming language.
Python is a high-level programming language, which means it is designed to be easy to read and write. This makes it a popular choice for beginners and experts alike.
Python is an interpreted language, which means that instead of compiling the code into machine language before running it, the code is interpreted by the Python interpreter at runtime. This allows for rapid development and easy debugging.
Python is an object-oriented language, which means it supports OOP concepts like inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism, which we will look into in our further journey. This makes it easier to write modular, reusable code.
Python is dynamically typed, which means that the type of a variable is inferred at runtime, rather than being explicitly declared in the code. This allows for more flexibility and quicker development, but can sometimes lead to errors that might have been caught with static typing.
Cross-platform: Python is a cross-platform language, which means that code written on one platform (e.g., Windows) can run on another platform (e.g., Linux) without modification, as long as the appropriate Python interpreter is installed.
Like any programming language, Py has its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision about whether Python is the right language for your project. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at the pros and cons of using Py and how it compares to other popular programming languages. So, let’s dive in and explore what makes Python so great, and where it falls short.
GIL limitation: Python has a Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) that limits its ability to take full advantage of multi-core processors, which can cause performance issues in some cases.
Python is like a Swiss Army Knife of programming languages, with a wide range of applications that make it a favourite among developers worldwide. From building websites and games to analysing data and controlling robots, Py has found its way into almost every field. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at some of the most interesting and diverse applications of Python that will make you see this language in a whole new light.
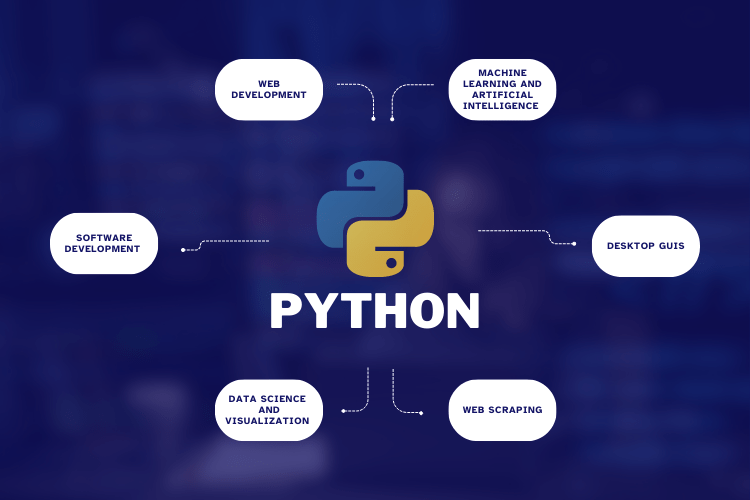
Python has a number of frameworks like Django and Flask that make it easy to build complex web applications. Popular websites like Instagram and Spotify are built using this programing language.
Python’s extensive library support and simplicity make it a popular language for machine learning and artificial intelligence applications. Libraries like TensorFlow, Keras, and PyTorch make it easy to build complex neural networks and train machine learning models.
Py has a range of libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib that make it easy to analyse and visualize data. These libraries are widely used in data science, research, and data analysis.
Python is also used to create games. Popular games like Civilization IV and Battlefield 2 have been built using this programming language.
Python is used to program robots and control their movements. For example, the Robot Operating System (ROS) is a popular platform for programming robots using Python.
And that’s a wrap for today’s blog! We’ve covered a lot of ground, from Python’s quirky naming origins to its diverse range of applications in various industries.
We also discussed the pros and cons of using Python, so you can make an informed decision about whether it’s the right language for your project. But wait, there’s more!
In our next blog post, we’ll dive deeper into the key components and building blocks of Python (add link), so you can start building your own amazing applications. Stay tuned and be sure to check it out! Thanks for joining us today, happy coding, and follow 1stepgrow!
We provide online certification in Data Science and AI, Digital Marketing, Data Analytics with a job guarantee program. For more information, contact us today!
Courses
1stepGrow
Anaconda | Jupyter Notebook | Git & GitHub (Version Control Systems) | Python Programming Language | R Programming Langauage | Linear Algebra & Statistics | ANOVA | Hypothesis Testing | Machine Learning | Data Cleaning | Data Wrangling | Feature Engineering | Exploratory Data Analytics (EDA) | ML Algorithms | Linear Regression | Logistic Regression | Decision Tree | Random Forest | Bagging & Boosting | PCA | SVM | Time Series Analysis | Natural Language Processing (NLP) | NLTK | Deep Learning | Neural Networks | Computer Vision | Reinforcement Learning | ANN | CNN | RNN | LSTM | Facebook Prophet | SQL | MongoDB | Advance Excel for Data Science | BI Tools | Tableau | Power BI | Big Data | Hadoop | Apache Spark | Azure Datalake | Cloud Deployment | AWS | GCP | AGILE & SCRUM | Data Science Capstone Projects | ML Capstone Projects | AI Capstone Projects | Domain Training | Business Analytics
WordPress | Elementor | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO | Technical SEO | Content SEO | SEM | PPC | Social Media Marketing | Email Marketing | Inbound Marketing | Web Analytics | Facebook Marketing | Mobile App Marketing | Content Marketing | YouTube Marketing | Google My Business (GMB) | CRM | Affiliate Marketing | Influencer Marketing | WordPress Website Development | AI in Digital Marketing | Portfolio Creation for Digital Marketing profile | Digital Marketing Capstone Projects
Jupyter Notebook | Git & GitHub | Python | Linear Algebra & Statistics | ANOVA | Hypothesis Testing | Machine Learning | Data Cleaning | Data Wrangling | Feature Engineering | Exploratory Data Analytics (EDA) | ML Algorithms | Linear Regression | Logistic Regression | Decision Tree | Random Forest | Bagging & Boosting | PCA | SVM | Time Series Analysis | Natural Language Processing (NLP) | NLTK | SQL | MongoDB | Advance Excel for Data Science | Alteryx | BI Tools | Tableau | Power BI | Big Data | Hadoop | Apache Spark | Azure Datalake | Cloud Deployment | AWS | GCP | AGILE & SCRUM | Data Analytics Capstone Projects
Anjanapura | Arekere | Basavanagudi | Basaveshwara Nagar | Begur | Bellandur | Bommanahalli | Bommasandra | BTM Layout | CV Raman Nagar | Electronic City | Girinagar | Gottigere | Hebbal | Hoodi | HSR Layout | Hulimavu | Indira Nagar | Jalahalli | Jayanagar | J. P. Nagar | Kamakshipalya | Kalyan Nagar | Kammanahalli | Kengeri | Koramangala | Kothnur | Krishnarajapuram | Kumaraswamy Layout | Lingarajapuram | Mahadevapura | Mahalakshmi Layout | Malleshwaram | Marathahalli | Mathikere | Nagarbhavi | Nandini Layout | Nayandahalli | Padmanabhanagar | Peenya | Pete Area | Rajaji Nagar | Rajarajeshwari Nagar | Ramamurthy Nagar | R. T. Nagar | Sadashivanagar | Seshadripuram | Shivajinagar | Ulsoor | Uttarahalli | Varthur | Vasanth Nagar | Vidyaranyapura | Vijayanagar | White Field | Yelahanka | Yeshwanthpur
Mumbai | Pune | Nagpur | Delhi | Gurugram | Chennai | Hyderabad | Coimbatore | Bhubaneswar | Kolkata | Indore | Jaipur and More